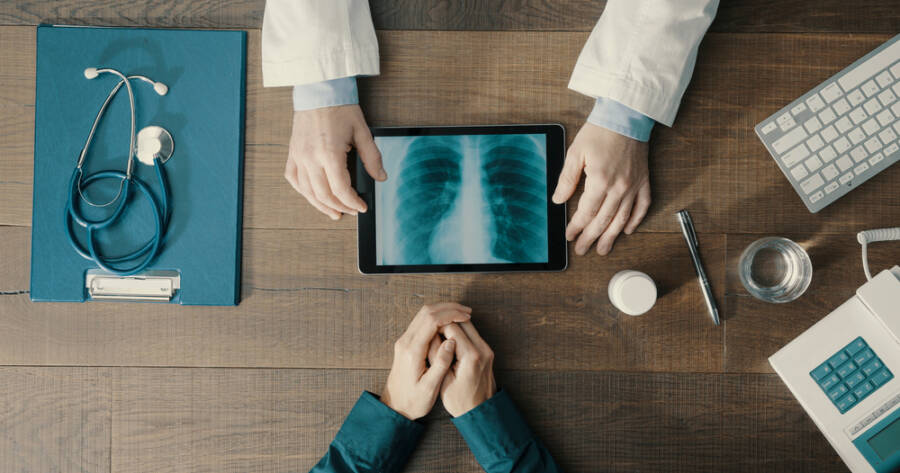
Lung cancer, once considered a formidable adversary, is now yielding to groundbreaking advancements in early detection, targeted therapies, and innovative treatment strategies. These developments are not only improving survival rates but also enhancing the quality of life for many patients. As technology evolves, these groundbreaking tools offer hope in reducing mortality rates and improving patient outcomes. Understanding these advancements reveals how they may revolutionize lung cancer detection.
The Importance of Early Detection
Detecting lung cancer early is crucial for enhancing the chances of successful treatment and increasing survival rates. Lung cancer is notorious for its subtle early symptoms, frequently leading to late-stage diagnoses. Early detection can significantly impact treatment options, often allowing for less invasive and more effective interventions. It may offer patients a better quality of life and extend survival possibilities, positioning early screening as an integral component of cancer care.
With technology advancing rapidly, the medical community is keen to harness new tools for early detection. Improved screening techniques could catch malignancies before they progress to advanced stages. This paradigm shift in lung cancer diagnosis emphasizes the value of regular screenings, especially for high-risk populations. Many emerging technologies aim to bring these benefits to patients, providing wider accessibility and accuracy in detection.
Low-Dose CT Scans: A Step Forward
Low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans have become a significant advancement in lung cancer screening technology. These scans provide detailed images of the lungs, potentially identifying nodules or masses at early stages. By utilizing a lower dose of radiation compared to standard CT scans, they minimize exposure risks, making them suitable for routine checks. Data suggest that low-dose CT scans can indeed reduce lung cancer mortality among high-risk groups.
The adoption of low-dose CT screening has had a noteworthy impact on early detection rates. Individuals with a history of heavy smoking or occupational exposure may benefit the most from these scans. Detecting abnormalities early allows for timely intervention strategies, including surveillance or biopsy. Collaboration between healthcare professionals ensures that findings from low-dose scans translate into precise, actionable medical decisions, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Liquid Biopsies: The New Frontier
Liquid biopsy technology represents a promising frontier in lung cancer diagnostics. This non-invasive test analyzes circulating tumor DNA in the bloodstream, possibly offering early identification of cancerous changes. By detecting genetic modifications linked with lung cancer, liquid biopsies may provide insights without the need for traditional surgical procedures. This method could allow for more frequent monitoring and quicker detection of disease progression or recurrence.
While liquid biopsy technology remains in developmental phases, its potential application in routine lung cancer screening is noteworthy. Early studies suggest it might complement other diagnostic tools, enhancing comprehensive cancer care. By evaluating specific biomarkers, liquid biopsies could offer tailored treatment insights and personalized patient care plans. As research and technological capabilities progress, liquid biopsies may become a staple in early lung cancer detection strategies.
AI and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms have begun to reshape lung cancer detection, improving both accuracy and efficiency. These technologies analyze vast datasets and medical imaging to identify patterns that might escape human observation. By processing and interpreting diagnostic scans at incredible speeds, AI could reduce diagnostic errors and enhance early detection. Machine learning models trained on extensive datasets offer predictive insights into cancer progression.
AI applications in lung cancer diagnostics demonstrate significant potential in interpreting complex imaging data. By highlighting suspicious areas or suggesting probabilities of malignancy, AI assists radiologists and pathologists in making informed decisions. Moreover, AI can aid in predicting patient outcomes, informing personalized treatment plans. As these technologies evolve, they hold promise for refining the accuracy and speed of lung cancer diagnoses.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite technological advances, challenges in early lung cancer detection persist, necessitating careful consideration. Access to advanced diagnostic tools may vary, leading to discrepancies in early detection capabilities across different regions. Additionally, false positives or incidental findings can arise, posing potential ethical and clinical dilemmas. Establishing appropriate follow-up protocols and care pathways remains essential to addressing such concerns effectively.
Integrating new technologies also demands collaboration across multiple healthcare disciplines. Ensuring that diagnostic results lead seamlessly to appropriate interventions and treatments requires a coordinated effort. Healthcare providers must remain vigilant against over-relying on technology without clinical validation. Ensuring a balanced approach by harmonizing technological insights with medical expertise may enhance early detection’s impact on patient care.
Advancing the Paradigm of Lung Cancer Detection
Advancements in technology hold promise for transforming lung cancer detection, potentially improving outcomes through earlier diagnosis. Emerging tools, such as low-dose CT scans, liquid biopsies, and AI-driven diagnostics, offer groundbreaking avenues for enhancing detection capabilities.
While challenges remain, ongoing innovation continues to drive meaningful progress in this critical area of healthcare. By understanding and embracing these technologies, medical professionals and patients together may pave the way to more effective lung cancer management. Staying informed about these developments encourages an optimistic outlook on the future of cancer care.