Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions worldwide. It is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage cushioning the ends of bones in joints gradually wears down. This condition primarily affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, spine, and hands, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. See how it compares with rheumatoid arthritis and explore care tips.
Understanding Osteoarthritis
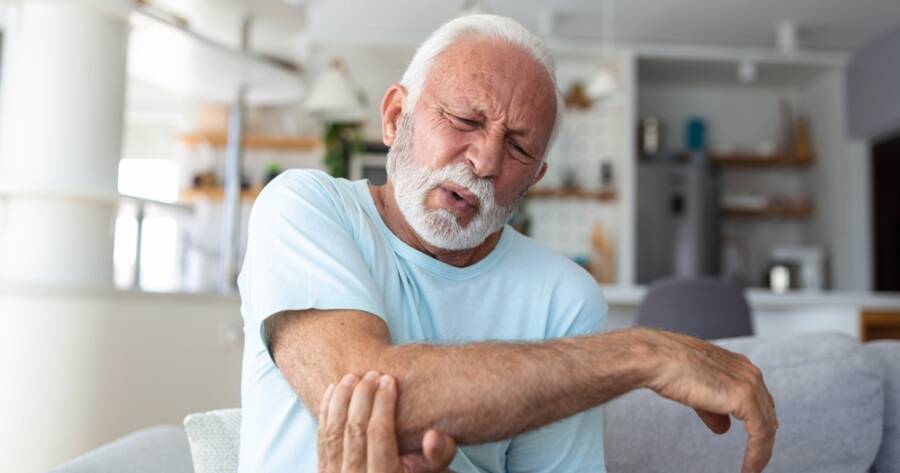
Osteoarthritis (OA) is often termed a “wear-and-tear” disease, largely because it results from the gradual deterioration of joint cartilage over time. This condition primarily affects older adults, although injury or excessive joint use can trigger it in younger individuals.
OA typically manifests through pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, most commonly affecting the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of OA is the degeneration of cartilage, which normally serves to cushion the joints. A combination of factors, such as genetics, age, weight, and previous injuries, could elevate the risk of developing OA.
Being overweight might stress weight-bearing joints, while genetic predispositions could affect the body’s ability to repair joint tissues effectively.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of OA can vary widely, but typical indicators include joint pain during or after movement, tenderness in the joints, stiffness, and a grating sensation when moving the joint. In some cases, bone spurs might form around the affected joint, leading to further discomfort.
Management and Care Tips
Managing OA might involve a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and physical therapy. Weight management through a balanced diet and regular exercise, if feasible, may reduce stress on the joints.
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications might provide temporary relief. Low-impact activities like swimming or walking could help maintain joint flexibility and overall fitness.
Exploring Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), unlike OA, is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and potential damage to joint tissue. RA can occur at any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in middle-aged individuals and frequently affects women more than men.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of RA remains uncertain, though it likely involves a mix of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genetic markers might make one more susceptible to developing RA, and environmental triggers such as smoking or infections could further heighten risk.
Recognizing Symptoms
RA often begins with subtle symptoms that can mimic other diseases, making early diagnosis challenging. Common warning signs include tender, warm, swollen joints, and morning stiffness that lasts longer than 30 minutes. Fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite might also accompany these symptoms. Unlike OA, RA typically affects joints symmetrically on both sides of the body.
Pathways to Care
The management strategy for RA often includes medications aimed at reducing inflammation and suppressing immune system activity. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) might slow the progression, while biologic agents could target specific immune pathways. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may help maintain function and optimize quality of life.
Integrative Approaches to Care
While OA and RA are distinct conditions, some integrative care approaches could benefit individuals with either condition. Mind-body therapies like yoga and tai chi, although not cures, might offer gentle ways to improve flexibility and reduce stress. Nutritional support, guided by a healthcare provider, can also be a valuable component of a holistic approach to arthritis management.
The Role of Diet and Supplements
Though direct evidence is limited, some individuals might find that anti-inflammatory diets — rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids — support their joint health. Supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin are sometimes discussed as options, but individuals should consult healthcare professionals due to mixed evidence on their effectiveness.
Learn More Today!
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis present unique challenges but understanding their differences can empower individuals to seek appropriate interventions. Through tailored medical treatments and supportive lifestyle practices, many people with arthritis may find ways to manage symptoms and enhance their well-being. As always, consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial for developing personalized care plans that address individual needs and circumstances.