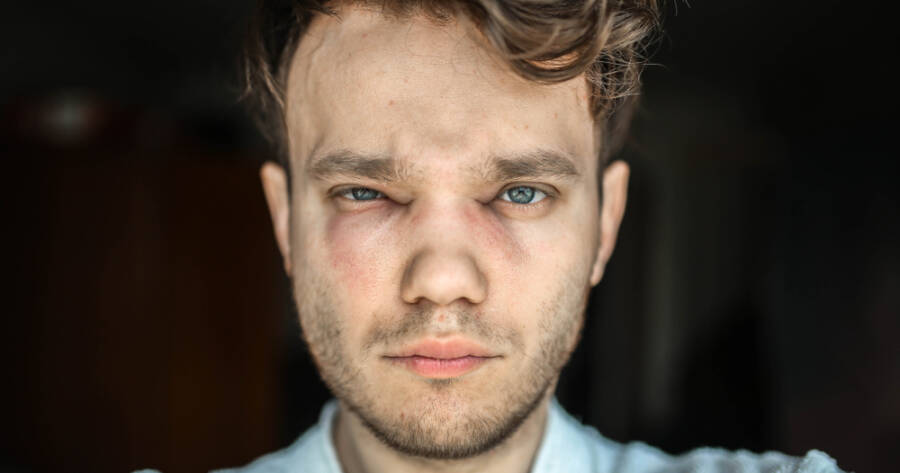
Angioedema is characterized by swelling beneath the skin, often affecting areas such as the face, lips, and throat. Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management of this condition. If you or someone you love is struggling to manage this condition, you can learn more about angioedema symptoms and the available treatment options!
What Is Angioedema?
Angioedema is a condition where the deeper layers of the skin, often in the face, lips, throat, and sometimes the arms and legs, swell up. It is similar to hives (urticaria), but instead of being on the surface of the skin, the swelling happens deeper down. This swelling can be caused by various factors, including allergies, medications, or other underlying health conditions.
The swelling usually occurs suddenly and can range from mild to severe. In some cases, if the throat or airways swell, it can lead to difficulty breathing, which makes prompt treatment very important.
Common Symptoms of Angioedema
The most common symptom of angioedema is swelling, which can appear on different parts of the body. The swelling may develop rapidly and last anywhere from a few hours to a few days. Typically, the areas most affected are:
- Face: This includes the eyes, lips, and tongue. Swelling in the face can lead to discomfort and may affect one side more than the other.
- Throat: Swelling here can be dangerous because it may block the airways, making it harder to breathe.
- Limbs: Some people may experience swelling in the hands, feet, or legs.
Other signs may include pain or a feeling of tightness in the affected area. In some cases, angioedema can also occur alongside hives, where raised, red welts appear on the surface of the skin.
Causes and Triggers of Angioedema
Angioedema can have several causes, and understanding the triggers is key to managing the condition. Some of the most common causes of angioedema include:
- Allergic reactions: This is one of the most frequent triggers. Common allergens, like certain foods, medications, insect stings, and animal dander, can cause an allergic reaction that leads to swelling.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as ACE inhibitors used for blood pressure, can trigger angioedema in some individuals. This is a rare but serious side effect.
- Infections: Sometimes, an infection can cause an immune response that leads to swelling beneath the skin.
- Hereditary factors: In some people, angioedema runs in families. This is known as hereditary angioedema, a rare genetic condition.
- Stress or temperature changes: Emotional stress or exposure to very hot or cold temperatures can also trigger the condition.
How Is Angioedema Diagnosed?
To diagnose angioedema, healthcare providers typically start by taking a detailed medical history, including any recent allergies or medications. A physical exam is performed to identify the areas of swelling.
If necessary, further tests may be conducted. The use of blood tests can rule out other conditions and identify the cause. In some cases, genetic testing may be recommended to confirm hereditary angioedema, while skin tests can help pinpoint specific allergens.
Effective Treatments for Angioedema
Treating angioedema depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause. For most cases, the swelling will resolve on its own within a few days. However, in more severe cases, treatment may be necessary. Here are some common treatment options:
- Antihistamines: These are often the first line of treatment. Antihistamines can help reduce swelling and discomfort by blocking the histamines that cause the allergic reaction.
- Corticosteroids: For more severe cases, oral corticosteroids like prednisone may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Epinephrine: In cases where the throat swells, making breathing difficult, an injection of epinephrine (adrenaline) may be required to quickly reduce the swelling and open the airways.
- Omalizumab (Xolair): For idiopathic or chronic angioedema, Omalizumab, an injectable medication used to treat allergic asthma, can help manage symptoms by regulating the immune response. It works by targeting immunoglobulin E (IgE), a substance that can trigger allergic reactions.
- Medications for hereditary angioedema: If the condition is hereditary, specific treatments like C1 esterase inhibitors may be prescribed to control the symptoms and prevent future episodes.
It’s important to avoid known triggers. If the swelling is due to an allergic reaction, identifying and avoiding the allergen is crucial for preventing further episodes.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and manage the condition. Immediate medical attention is particularly important if the swelling affects the throat, as it could result in a life-threatening airway obstruction.
Managing Angioedema Long-Term
For people with chronic angioedema or those who experience frequent episodes, long-term management may be needed. This includes working with a doctor to:
- Identify triggers and avoid them
- Take preventive medications if needed
- Carry emergency medications, such as an epinephrine injector, especially if there is a risk of airway swelling
Education is also an important aspect of long-term management. Patients should be informed about the signs of severe reactions and when to seek urgent care. With proper care and monitoring, many people with angioedema can manage their condition effectively.
Manage Your Angioedema
Angioedema is a condition that can range from mild swelling to severe reactions, sometimes threatening the airway. Understanding the symptoms and causes is essential for managing the condition.
Whether caused by allergies, medications, or hereditary factors, recognizing the triggers and seeking appropriate treatment can make a big difference. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of angioedema, seek medical advice to ensure the best possible care.